Eat Well, Live Well: A Comprehensive Guide to Healthy Eating and Nutrition
Healthy eating and nutrition are fundamental to maintaining overall well-being and preventing chronic diseases. By choosing nutrient-dense foods, individuals can improve their physical health, mental clarity, and energy levels. From plant-based diets to intermittent fasting, discover the diverse options available to support a healthier lifestyle.
1Plant-Based Diet
0 votes
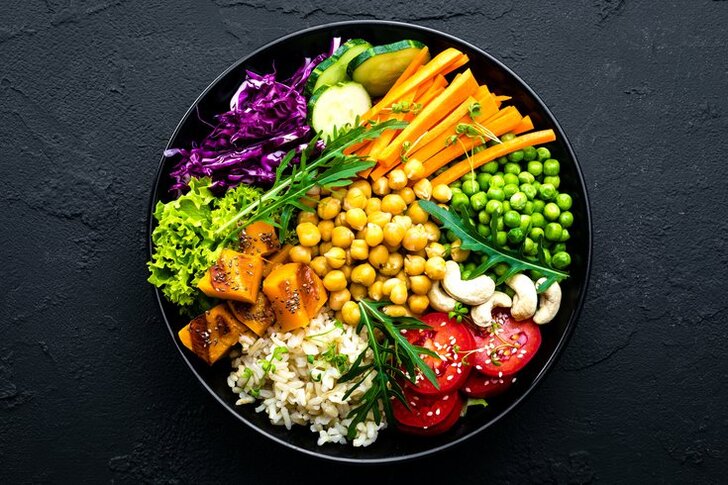

A plant-based diet focuses on consuming foods primarily from plants, including vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, oils, whole grains, legumes, and beans. This diet minimizes or eliminates animal products, emphasizing whole, unprocessed plant foods. Advocates for plant-based diets often cite health benefits such as reduced risks of heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and certain cancers. Moreover, plant-based eating can contribute to weight management, improved digestion, and increased energy levels. Ethical and environmental considerations also play a significant role, as plant-based diets typically have a lower carbon footprint and avoid animal welfare issues. Transitioning to a plant-based diet involves mindful planning to ensure all essential nutrients, such as protein, iron, calcium, and vitamin B12, are adequately obtained. Overall, a plant-based diet can be a sustainable and healthful choice when balanced and varied.
0
Do you agree? 0% of people agree with your point of view!
2Mediterranean Diet
0 votes

The Mediterranean diet is inspired by the traditional eating patterns of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, such as Greece, Italy, and Spain. It emphasizes the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and healthy fats, particularly olive oil. Moderate amounts of fish, poultry, dairy, and red wine are included, while red meat and sweets are limited. This diet is renowned for its heart health benefits, attributed to its high content of monounsaturated fats, antioxidants, and fiber. Studies have shown that the Mediterranean diet can reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases, improve cholesterol levels, and support healthy weight management. It also promotes brain health and may help prevent cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. The Mediterranean diet is more of a lifestyle than a strict dietary regimen, encouraging regular physical activity and social meals. Its diverse and flavorful foods make it a popular and sustainable way of eating.
0
Do you agree? 0% of people agree with your point of view!
3DASH Diet
0 votes

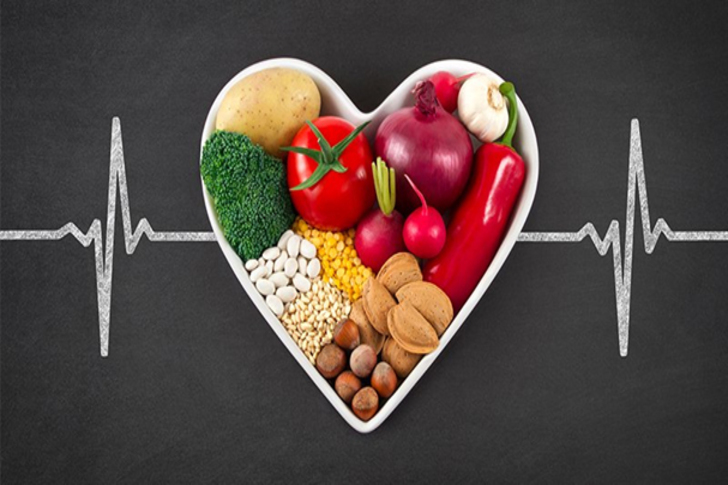
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet is designed to combat high blood pressure and promote cardiovascular health. It emphasizes the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy while limiting salt, red meat, and added sugars. The DASH diet is rich in potassium, magnesium, and calcium, which are crucial for blood pressure regulation. Studies have shown that the DASH diet can effectively lower blood pressure, reduce LDL cholesterol levels, and decrease the risk of heart disease and stroke. Additionally, it supports weight management and overall health by encouraging balanced, nutrient-dense meals. The diet’s flexibility and emphasis on whole foods make it easy to follow and adapt to individual preferences and dietary needs. Despite its benefits, individuals may find it challenging to reduce sodium intake and avoid processed foods. However, the DASH diet is widely regarded as one of the healthiest eating plans available.
0
Do you agree? 0% of people agree with your point of view!
4Ketogenic Diet
0 votes

The ketogenic diet, or keto diet, is a low-carb, high-fat diet that aims to induce a state of ketosis in the body, where fat is used as the primary energy source instead of carbohydrates. This diet significantly reduces carbohydrate intake, typically to less than 50 grams per day, and increases fat intake to around 70-80% of total daily calories, with moderate protein consumption. The keto diet has gained popularity for its potential to promote rapid weight loss, improve insulin sensitivity, and manage certain health conditions such as epilepsy, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. However, it requires careful planning to ensure nutritional adequacy and avoid potential side effects like nutrient deficiencies, electrolyte imbalances, and gastrointestinal issues. The diet’s restrictive nature may also pose challenges for long-term adherence. Despite these considerations, many individuals find the keto diet effective for achieving their health and weight goals.
0
Do you agree? 0% of people agree with your point of view!
5Paleo Diet
0 votes

The paleo diet, also known as the caveman diet, is based on the eating habits of our Paleolithic ancestors. It emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods such as lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, while excluding dairy, grains, legumes, and processed foods. The paleo diet advocates believe that modern diets are mismatched with our genetic makeup, leading to chronic diseases and health issues. By returning to a more ancestral way of eating, the paleo diet aims to improve health outcomes. Proponents claim benefits such as weight loss, reduced inflammation, improved digestion, and increased energy levels. The diet also focuses on high protein intake, healthy fats, and low glycemic index foods, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and support muscle growth. Critics of the paleo diet point out the lack of long-term research and the exclusion of entire food groups, which may lead to nutrient deficiencies. Nonetheless, many individuals find the paleo diet effective for their health and fitness goals.
0
Do you agree? 0% of people agree with your point of view!
6Intermittent Fasting
0 votes

Intermittent fasting (IF) is an eating pattern that cycles between periods of eating and fasting. Unlike traditional diets that focus on what to eat, IF focuses on when to eat. Common methods include the 16/8 method (fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window), the 5:2 diet (eating normally for five days and restricting calories for two non-consecutive days), and the eat-stop-eat approach (24-hour fasts once or twice a week). Intermittent fasting can promote weight loss, improve metabolic health, and extend lifespan by optimizing cellular repair processes and hormone levels. Research suggests that IF can enhance insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and improve cardiovascular health. It may also offer neuroprotective benefits and support brain health. However, it may not be suitable for everyone, particularly those with certain medical conditions or who are pregnant. Adopting intermittent fasting should be done gradually and under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure safety and effectiveness.
0
Do you agree? 0% of people agree with your point of view!






Recent Comments